IT STUDY LOG
[컨테이너 오케스트레이션] 02. 쿠버네티스 워크로드 본문
# 학습 목표
- 컨테이너 오케스트레이션이 무엇인지 이해할 수 있다.
- 쿠버네티스의 간단한 작동 원리를 이해할 수 있다.
- 쿠버네티스 리소스 명세를 작성할 수 있다.
- 파드 명세를 작성할 수 있다.
- 디플로이먼트 명세를 작성할 수 있다.
- 서비스를 이용해 파드를 노출할 수 있다.
- kubectl 명령어를 사용하여 리소스의 생성, 삭제, 조회를 할 수 있다.
- kubectl 명령어를 사용하여 롤아웃 관련 작업을 진행할 수 있다.
- 롤링 배포 현황을 확인할 수 있다.
- 새로운 버전에 문제가 발생했을 때 롤백할 수 있다.
(이하 advanced)
- liveness probe를 이용하여 파드의 health check를 할 수 있다.
- 쿠버네티스가 Stateful한 애플리케이션을 다루는 방법을 이해할 수 있다.
- 쿠버네티스에서 인그레스를 이용한 HTTP 기반 라우팅을 적용할 수 있다.
- helm 패키지 매니저를 사용할 수 있다.
# 학습 내용
1. 파드 (Pods)
파드란?

- 쿠버네티스의 배포 가능한 가장 작은 컴퓨팅 유닛으로, 그 자체로 하나의 논리적인 호스트
- 파드는 다음을 포함할 수 있으며 마치 도커 컨테이너처럼 파드 내에서 다음 요소들은 격리됨
- 하나 이상의 애플리케이션 컨테이너
- IP 주소
- 볼륨과 같은 공유 스토리지
워크로드란?
클라우드 분야에의 워크로드
- “어떤 애플리케이션을 실행할 때 필요한 IT 리소스의 집합”이라는 의미로 통용
쿠버네티스에서 워크로드
- “쿠버네티스 상에서 작동되는 애플리케이션”을 의미
- 쿠버네티스에서는 “워크로드 리소스”를 만들기 위해 보통 YAML 파일과 같은 리소스 정의 파일을 사용
- 파드를 생성하기 위해 파드를 정의할 때 다음과 같은 형태의 YAML 파일을 사용 가능 (아래 YAML을 따라서 만들고, 적당한 디렉토리에 simple-pod.yaml로 저장)
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
- apiVersion: v1
- kind: Pod
- metadata (ObjectMeta) : 표준 객체의 메타 데이터로, 사용자가 생성해야 하는 모든 개체를 포함하는 모든 지속형 리소스에 있어야 하는 메타데이터
- name (string) : 리소스 생성할 때 필요하며 네임스페이스 내에서 고유해야 함, 수정 불가
- generateName (string) : 이름 필드가 제공되지 않은 경우 고유한 이름을 생성하기 위한 선택적 속성
- namespace (string) : 각 이름이 고유해야 하는 공간
- labels (map[string]string) : 개체 구성화, 범주화에 사용할 수 있는 문자열 키 및 값의 맵
- annotations (map[string]string) : 임의의 메타데이터를 저장하고 검색하기 위해 외부 도구로 설정할 수 있는 리소스와 함께 저장되는 구조화되지 않은 키값 맵
- spec (PodSpec) : 파드의 명세로 파드가 동작해야할 내용을 작성
- containers ([]Container), 필수: Pod에 속한 컨테이너 목록으로 하나 이상의 컨테이너가 존재해야 함. 현재 컨테이너를 추가, 제거, 업데이트 불가
- initContainers ([]Container) : Pod에 속한 초기화 컨테이너 목록으로 컨테이너가 시작되기 전에 순서대로 실행됨. 초기화 컨테이너는 현재 추가, 제거, 업데이트 불가
- ephemeralContainers ([]EphemeralContainer) : 포드에서 실행되는 임시 컨테이너 목록
- imagePullSecrets ([]LocalObjectReference) : PodSpec에서 사용하는 이미지를 가져오는 데 사용할 동일한 네임스페이스의 비밀에 대한 참조 목록(선택 사항)
- enableServiceLinks (boolean) : 서비스에 대한 정보를 Docker 링크의 구문과 일치하는 포드의 환경 변수에 삽입해야 하는지 여부를 나타내며 기본값은 true
- os (PodOS) : 팟(Pod)에 있는 컨테이너의 OS를 지정하고 설정된 경우 일부 포드 및 컨테이너 필드가 제한됨
- os.name (string), 필수: 이름은 운영 체제의 이름입니다. 현재 지원되는 값은 linux 및 windows
- status (PodStatus) : 포드의 가장 최근에 관찰된 상태며, 데이터는 최신이 아닐 수 있음. 시스템에 의해 작성되며 읽기 전용
파드 적용하기
Step 1 : 파드 정의 파일을 실제로 만들기 위해 kubectl apply <yaml 파일> 명령어 사용
$ kubectl apply -f simple-pod.yaml
pod/nginx createdStep 2 : kubectl get pods 명령어로 상태 확인
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 8s
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx 1/1 Running 0 30sStep 3 : kubectl describe <pods 명>으로 상태 확인
$ kubectl describe pod/nginx
Name: nginx
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Service Account: default
Node: minikube/192.168.49.2
Start Time: Thu, 18 May 2023 13:28:12 +0900
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.0.3
IPs:
IP: 10.244.0.3
Containers:
nginx:
Container ID: docker://c8a7f88bd42a6b3a89ecb7b4d8a57d79487f31f1a4efb95519a22640e70a80f1
Image: nginx:1.14.2
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:f7988fb6c02e0ce69257d9bd9cf37ae20a60f1df7563c3a2a6abe24160306b8d
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Thu, 18 May 2023 13:28:45 +0900
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-8mvkp (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
kube-api-access-8mvkp:
Type: Projected (a volume that contains injected data from multiple sources)
TokenExpirationSeconds: 3607
ConfigMapName: kube-root-ca.crt
ConfigMapOptional: <nil>
DownwardAPI: true
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 2m9s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/nginx to minikube
Normal Pulling 2m8s kubelet Pulling image "nginx:1.14.2"
Normal Pulled 100s kubelet Successfully pulled image "nginx:1.14.2" in 28.39091584s (28.390921632s including waiting)
Normal Created 96s kubelet Created container nginx
Normal Started 96s kubelet Started container nginxStep 4 : kubectl delete 명령어를 사용해 파드 리소스 삭제
# example
# pod.json에 지정된 유형 및 이름을 사용하여 파드 삭제
$ kubectl delete -f ./pod.json
# 유예 시간 없이 즉시 파드 삭제
$ kubectl delete pod unwanted --now
# "baz", "foo"와 동일한 이름을 가진 파드와 서비스 삭제
$ kubectl delete pod,service baz foo
# name=myLabel 라벨을 가진 파드와 서비스 삭제
$ kubectl delete pods,services -l name=myLabel
# my-ns 네임스페이스 내 모든 파드와 서비스 삭제
$ kubectl -n my-ns delete pod,svc --all
# awk pattern1 또는 pattern2에 매칭되는 모든 파드 삭제
$ kubectl get pods -n mynamespace --no-headers=true | awk '/pattern1|pattern2/{print $1}' | xargs kubectl delete -n mynamespace pod$ kubectl delete pod,service nginx
pod "nginx" deleted
Error from server (NotFound): services "nginx" not found
$ kubectl get pods
No resources found in default namespace.
2. 디플로이먼트 (Deployment)
쿠버네티스에서 Deployment는 한글로 번역하지 않음
배포라고 하면 서비스의 노출을 떠올리지만, 쿠버네티스의 Deployment는 서비스 노출의 의미가 아닌 파드의 교체/배치(placement)와 관련된 명세를 뜻함
파드의 진실
- 쿠버네티스에서는 사실 직접 사용자가 개별 파드를 만들 일이 그리 많지 않음
- 왜냐하면 파드는 일시적이고, 언제나 삭제될 수 있음을 감안하고 만들기 때문
(예) 파드가 실행되는 공간인 노드가 만일 실패하는 경우, 그 안에서 실행되는 파드 역시 사용할 수 없게 됨

- 사실 컨테이너를 수동으로 만들고 관리하는 것은, 그냥 도커만 단독으로 사용해도 충분히 할 수 있는 일
- 쿠버네티스의 핵심은 컨테이너를 오케스트레이션하는 것으로, 파드 장애 시 자동 복구하거나, 복제하거나 하는 등의 일을 자동으로 처리하는 데에 있음
- AWS로 따지면 ECS(Elastic Container Service)가 하는 일과 비슷
- 컨테이너의 로드 밸런싱과 오토 스케일링과 같은 일을 담당
- 결론적으로, 파드는 디플로이먼트, 스테이트풀셋, 데몬셋을 이용해 관리하는 것이 바람직
- 해당 워크로드 리소스는 파드 템플릿을 항상 포함
디플로이먼트의 예시
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
# 여기서부터 파드 템플릿 시작
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
# 여기까지 파드 템플릿
디플로이먼트 리소스란?
- 디플로이먼트는 파드를 업데이트하기 위한 선언적 명세
- 디플로이먼트 리소스로 수행 가능한 일
- (레플리카셋, 즉 복제본 구성을 이용하여) 파드를 원하는 개수만큼 실행 가능
- (제어판 Control Plane을 이용하여) 파드를 업데이트 가능
- 파드를 롤백하는 것도 가능
리뷰: 다양한 배포 전략
- 애플리케이션의 여러 복제본이 존재할 경우, 이 각각의 복제본을 새 버전으로 업데이트하는 방법으로 다음과 같은 배포 전략이 존재
- 재생성 (Recreate): 이전 버전을 삭제하고 새 버전 생성
- 블루/그린 배포: 한 번에 이전 버전에서 새 버전으로 연결을 전환
- 롤링 배포: 이전 버전을 scale down하고, 새 버전을 scale up 하는 방식으로 단계별로 교체. 롤아웃(rollout)
- 카나리 배포: 새 버전이 잘 작동한다고 판단되면, 이전 버전을 교체
- 디플로이먼트는 파드의 복제본을 자동으로 업데이트하게 해주는 명세이므로, 쿠버네티스가 지원하는 배포 전략으로는 재생성(Recreate)과 롤링 배포(RollingUpdate) 방식을 선택 가능
Hands-on: 공식 문서를 통한 디플로이먼트 실습
디플로이먼트 적용하기
$ kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/nginx-deployment created
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-deployment-85996f8dbd-2wp55 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 35s
nginx-deployment-85996f8dbd-cg8w5 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 35s
nginx-deployment-85996f8dbd-tvss6 0/1 ContainerCreating 0
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-deployment-85996f8dbd-2wp55 1/1 Running 0 2m50s
nginx-deployment-85996f8dbd-cg8w5 1/1 Running 0 2m50s
nginx-deployment-85996f8dbd-tvss6 1/1 Running 0 2m50s
$ kubectl delete pod -l app="nginx"
pod "nginx-deployment-85996f8dbd-2wp55" deleted
pod "nginx-deployment-85996f8dbd-cg8w5" deleted
pod "nginx-deployment-85996f8dbd-tvss6" deleted
반드시 해봐야 할 실습
# deployment 생성
$ kubectl create deployment kubernetes-bootcamp --image=gcr.io/google-samples/kubernetes-bootcamp:v1
# deployment 목록 보기
$ kubectl get deployments
# 프록시
$ echo -e "\n\n\n\e[92mStarting Proxy. After starting it will not output a response. Please click the first Terminal Tab\n";
$ kubectl proxy
$ curl http://localhost:8001/version
{
"major": "1",
"minor": "26",
"gitVersion": "v1.26.3",
"gitCommit": "9e644106593f3f4aa98f8a84b23db5fa378900bd",
"gitTreeState": "clean",
"buildDate": "2023-03-15T13:33:12Z",
"goVersion": "go1.19.7",
"compiler": "gc",
"platform": "linux/amd64"
}
# 파드명 찾기
$ export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods -o go-template --template '{{range .items}}{{.metadata.name}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}')
echo Name of the Pod: $POD_NAME
Name of the Pod: kubernetes-bootcamp-5485cc6795-kvq4f
# api를 통해 pods에 접근
$ curl http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/$POD_NAME/
{
"kind": "Pod",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
"name": "kubernetes-bootcamp-5485cc6795-kvq4f",
"generateName": "kubernetes-bootcamp-5485cc6795-",
"namespace": "default",
"uid": "25467dee-ffa6-49ae-85ac-9a0e3a40ad52",
"resourceVersion": "1374",
"creationTimestamp": "2023-05-18T10:52:35Z",
"labels": {
"app": "kubernetes-bootcamp",
"pod-template-hash": "5485cc6795"
},
"ownerReferences": [
{
"apiVersion": "apps/v1",
"kind": "ReplicaSet",
"name": "kubernetes-bootcamp-5485cc6795",
"uid": "907b96f8-fa24-4756-a2b3-fd34b418d38d",
"controller": true,
"blockOwnerDeletion": true
}
],
"managedFields": [
{
"manager": "kube-controller-manager",
"operation": "Update",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"time": "2023-05-18T10:52:35Z",
"fieldsType": "FieldsV1",
"fieldsV1": {
"f:metadata": {
"f:generateName": {},
"f:labels": {
".": {},
"f:app": {},
"f:pod-template-hash": {}
},
"f:ownerReferences": {
".": {},
"k:{\"uid\":\"907b96f8-fa24-4756-a2b3-fd34b418d38d\"}": {}
}
},
"f:spec": {
"f:containers": {
"k:{\"name\":\"kubernetes-bootcamp\"}": {
".": {},
"f:image": {},
"f:imagePullPolicy": {},
"f:name": {},
"f:resources": {},
"f:terminationMessagePath": {},
"f:terminationMessagePolicy": {}
}
},
"f:dnsPolicy": {},
"f:enableServiceLinks": {},
"f:restartPolicy": {},
"f:schedulerName": {},
"f:securityContext": {},
"f:terminationGracePeriodSeconds": {}
}
}
},
{
"manager": "kubelet",
"operation": "Update",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"time": "2023-05-18T10:53:02Z",
"fieldsType": "FieldsV1",
"fieldsV1": {
"f:status": {
"f:conditions": {
"k:{\"type\":\"ContainersReady\"}": {
".": {},
"f:lastProbeTime": {},
"f:lastTransitionTime": {},
"f:status": {},
"f:type": {}
},
"k:{\"type\":\"Initialized\"}": {
".": {},
"f:lastProbeTime": {},
"f:lastTransitionTime": {},
"f:status": {},
"f:type": {}
},
"k:{\"type\":\"Ready\"}": {
".": {},
"f:lastProbeTime": {},
"f:lastTransitionTime": {},
"f:status": {},
"f:type": {}
}
},
"f:containerStatuses": {},
"f:hostIP": {},
"f:phase": {},
"f:podIP": {},
"f:podIPs": {
".": {},
"k:{\"ip\":\"10.244.0.3\"}": {
".": {},
"f:ip": {}
}
},
"f:startTime": {}
}
},
"subresource": "status"
}
]
},
"spec": {
"volumes": [
{
"name": "kube-api-access-x7qnc",
"projected": {
"sources": [
{
"serviceAccountToken": {
"expirationSeconds": 3607,
"path": "token"
}
},
{
"configMap": {
"name": "kube-root-ca.crt",
"items": [
{
"key": "ca.crt",
"path": "ca.crt"
}
]
}
},
{
"downwardAPI": {
"items": [
{
"path": "namespace",
"fieldRef": {
"apiVersion": "v1",
"fieldPath": "metadata.namespace"
}
}
]
}
}
],
"defaultMode": 420
}
}
],
"containers": [
{
"name": "kubernetes-bootcamp",
"image": "gcr.io/google-samples/kubernetes-bootcamp:v1",
"resources": {},
"volumeMounts": [
{
"name": "kube-api-access-x7qnc",
"readOnly": true,
"mountPath": "/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount"
}
],
"terminationMessagePath": "/dev/termination-log",
"terminationMessagePolicy": "File",
"imagePullPolicy": "IfNotPresent"
}
],
"restartPolicy": "Always",
"terminationGracePeriodSeconds": 30,
"dnsPolicy": "ClusterFirst",
"serviceAccountName": "default",
"serviceAccount": "default",
"nodeName": "minikube",
"securityContext": {},
"schedulerName": "default-scheduler",
"tolerations": [
{
"key": "node.kubernetes.io/not-ready",
"operator": "Exists",
"effect": "NoExecute",
"tolerationSeconds": 300
},
{
"key": "node.kubernetes.io/unreachable",
"operator": "Exists",
"effect": "NoExecute",
"tolerationSeconds": 300
}
],
"priority": 0,
"enableServiceLinks": true,
"preemptionPolicy": "PreemptLowerPriority"
},
"status": {
"phase": "Running",
"conditions": [
{
"type": "Initialized",
"status": "True",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": "2023-05-18T10:52:35Z"
},
{
"type": "Ready",
"status": "True",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": "2023-05-18T10:53:02Z"
},
{
"type": "ContainersReady",
"status": "True",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": "2023-05-18T10:53:02Z"
},
{
"type": "PodScheduled",
"status": "True",
"lastProbeTime": null,
"lastTransitionTime": "2023-05-18T10:52:35Z"
}
],
"hostIP": "192.168.49.2",
"podIP": "10.244.0.3",
"podIPs": [
{
"ip": "10.244.0.3"
}
],
"startTime": "2023-05-18T10:52:35Z",
"containerStatuses": [
{
"name": "kubernetes-bootcamp",
"state": {
"running": {
"startedAt": "2023-05-18T10:53:01Z"
}
},
"lastState": {},
"ready": true,
"restartCount": 0,
"image": "gcr.io/google-samples/kubernetes-bootcamp:v1",
"imageID": "docker-pullable://gcr.io/google-samples/kubernetes-bootcamp@sha256:0d6b8ee63bb57c5f5b6156f446b3bc3b3c143d233037f3a2f00e279c8fcc64af",
"containerID": "docker://7da279e179c52aed7ff43f0f77f5fe0b29fe34d774ee531a9b5bc57dbd34acca",
"started": true
}
],
"qosClass": "BestEffort"
}
}%디플로이먼트(Deployment)로 스테이트리스 애플리케이션 실행하기
1. 디플로이먼트 선언 YAML 파일 작성, 리소스 생성 및 적용
# application/deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 2 # tells deployment to run 2 pods matching the template
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80# YAML 파일을 기반으로 디플로이먼트를 생성
$ kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/application/deployment.yaml
# 2. 디플로이먼트에 대한 정보 확인
$ kubectl describe deployment nginx-deployment
Name: nginx-deployment
Namespace: default
CreationTimestamp: Tue, 30 Aug 2016 18:11:37 -0700
Labels: app=nginx
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision=1
Selector: app=nginx
Replicas: 2 desired | 2 updated | 2 total | 2 available | 0 unavailable
StrategyType: RollingUpdate
MinReadySeconds: 0
RollingUpdateStrategy: 1 max unavailable, 1 max surge
Pod Template:
Labels: app=nginx
Containers:
nginx:
Image: nginx:1.14.2
Port: 80/TCP
Environment: <none>
Mounts: <none>
Volumes: <none>
Conditions:
Type Status Reason
---- ------ ------
Available True MinimumReplicasAvailable
Progressing True NewReplicaSetAvailable
OldReplicaSets: <none>
NewReplicaSet: nginx-deployment-1771418926 (2/2 replicas created)
No events.
# 3. 디플로이먼트에 의해 생성된 파드를 나열
$ kubectl get pods -l app=nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-deployment-1771418926-7o5ns 1/1 Running 0 16h
nginx-deployment-1771418926-r18az 1/1 Running 0 16h
# 4. 파드 정보 살피기
$ kubectl describe pod <pod-name>2. 디플로이먼트를 통해 Pod 업데이트
# application/deployment-update.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.16.1 # Update the version of nginx from 1.14.2 to 1.16.1
ports:
- containerPort: 80# 1. 새 YAML 파일을 적용
$ kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/application/deployment-update.yaml
#2. 디플로이먼트가 새 이름으로 파드를 생성하고 이전 파드를 삭제하는 것을 확인
$ kubectl get pods -l app=nginx3. 복제본을 통한 Scale out
# application/deployment-scale.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 4 # Update the replicas from 2 to 4
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80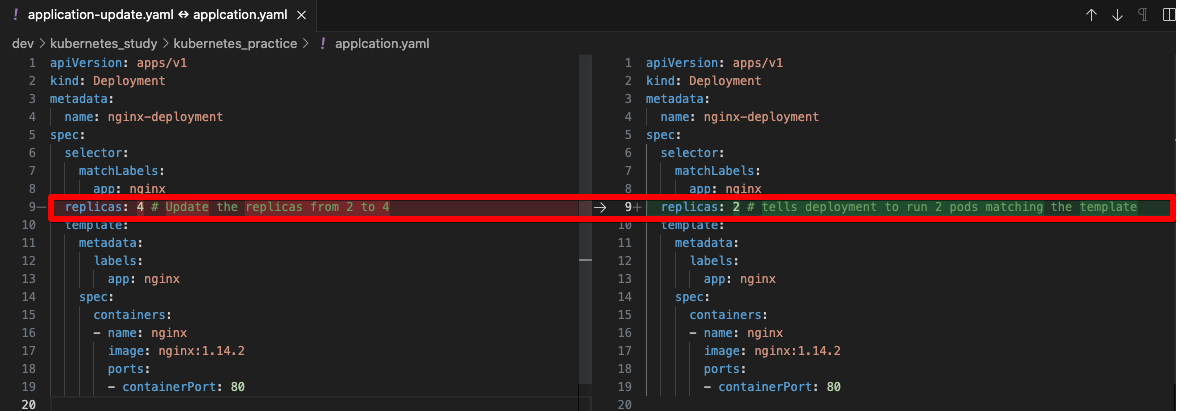
# 1. 새 YAML 파일을 적용
$ kubectl apply -f https://k8s.io/examples/application/deployment-scale.yaml
# 2. 디플로이먼트에 4개의 파드가 있는지 확인
$ kubectl get pods -l app=nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-deployment-148880595-4zdqq 1/1 Running 0 25s
nginx-deployment-148880595-6zgi1 1/1 Running 0 25s
nginx-deployment-148880595-fxcez 1/1 Running 0 2m
nginx-deployment-148880595-rwovn 1/1 Running 0 2m
# 3. 디플로이먼트 삭제하기
$ kubectl delete deployment nginx-deployment3. 서비스
파드를 외부로 노출시키기
- 클러스터 안에 파드는 각각 고유의 IP를 가지고 있지만, 직접 우리가 내부망에 접속할 수 없음
파드 안의 서비스를 외부로 노출하는 법
서비스 리소스를 사용하면 파드에서 실행 중인 애플리케이션을 클러스터 외부에서 접근 가능
- 또한 서비스를 사용하여 클러스터 내부에서 사용할 수 있는 서비스만 게시 가능
in 서비스, 로드밸런싱, 네트워킹 공식문서
- 쿠버네티스에서 서비스는 파드의 집합에 접근할 수 있는 정책을 정의하는 추상적 개념으로 서비스 리소스가 정의된 YAML 파일에 selector라는 것을 이용해 서비스할 대상 타깃을 설정 가능
- 디플로이먼트를 통해 파드의 복제본을 원하는 개수만큼 실행시킬 수 있으며 서비스 리소스는 이러한 파드 집합에 접근할 수 있게 하며, 파드가 교체되거나, 어떤 특정 파드에 문제가 생긴 경우에도 사용 가능한 파드를 찾아 알아서 접속할 수 있게 지원
서비스 만들어보기
# application-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
app: nginx # 배포하려는 파드를 지정(파드는 이미 실행중이어야 함)
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- name: nginx
protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80$ kubectl apply -f service.yaml
$ kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
cozserver LoadBalancer 10.111.181.232 <pending> 80:30185/TCP 12s
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 2m14s⚠️ minikube에서는 EXTERNAL-IP가 pending 상태로 진전이 되지 않는 경우?
- minikube tunnel 명령을 이용하면, EXTERNAL-IP가 127.0.0.1로 설정되며, 그때부터 http://localhost로 접속 가능
- 접속이 원활하지 않을 경우, tunnel을 중지하고 해당 명령을 다시 시도
# References
https://kubernetes.io/ko/docs/concepts/overview/components/
쿠버네티스 컴포넌트
쿠버네티스 클러스터는 컴퓨터 집합인 노드 컴포넌트와 컨트롤 플레인 컴포넌트로 구성된다.
kubernetes.io
https://kubernetes.io/ko/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/
파드
운영 수준의 컨테이너 오케스트레이션
kubernetes.io
https://kubernetes.io/ko/docs/tutorials/kubernetes-basics/explore/explore-intro/
파드와 노드 보기
<!DOCTYPE html> 목표 쿠버네티스 파드에 대해 배운다. 쿠버네티스 노드에 대해 배운다. 배포된 애플리케이션의 문제를 해결한다. 쿠버네티스 파드 모듈 2에서 배포를 생성했을 때, 쿠버네티스는 여
kubernetes.io
https://kubernetes.io/ko/docs/setup/production-environment/tools/kubeadm/install-kubeadm/
kubeadm 설치하기
이 페이지에서는 kubeadm 툴박스 설치 방법을 보여준다. 이 설치 프로세스를 수행한 후 kubeadm으로 클러스터를 만드는 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 kubeadm으로 클러스터 생성하기 페이지를 참고한다.
kubernetes.io
3. 쿠버네티스 클러스터 구축 - Docker & 쿠버네티스 클러스터 설치
서론 이전 포스팅에서 Ubuntu 설치 및 클러스터 구성을 위한 환경 설정을 진행했습니다. 이번 포스팅에서는 본격적으로 Docker 및 쿠버네티스를 설치하는 과정을 다루겠습니다. 1. Docker 설치 1. root
cla9.tistory.com
'devops bootcamp 4 > DevOps 인프라 관리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컨테이너 오케스트레이션] 04. 쿠버네티스 네트워크 (0) | 2023.05.22 |
|---|---|
| [컨테이너 오케스트레이션] 03. 쿠버네티스 구성 요소 (0) | 2023.05.22 |
| [컨테이너 오케스트레이션] 01. 쿠버네티스 주요 개념 (0) | 2023.05.17 |
| [Infrastructure as Code] 02. Terraform (0) | 2023.05.12 |
| [Infrastructure as Code] 01. Infrastructure as Code (코드형 인프라) (1) | 2023.05.12 |



